Übersicht
Casdoor is a UI-first Identity Access Management (IAM) / Single-Sign-On (SSO) platform with a web UI that supports OAuth 2.0, OIDC, SAML, CAS, LDAP, SCIM, WebAuthn, TOTP, MFA, RADIUS, Google Workspace, Active Directory, and Kerberos.
Casdoor dient sowohl der Web-UI als auch den Anmeldeanfragen von Anwendungsbenutzern.
Casdoor-Funktionen
-
Casdoor follows a frontend-backend separation architecture and is developed in Golang. It supports high concurrency, provides a web-based UI for management, and supports localization in over 10 languages.
-
Casdoor supports third-party application login options, such as GitHub, Google, QQ, and WeChat, and supports extending third-party login capabilities with plugins.
-
Casdoor unterstützt Autorisierungsmanagement basierend auf Casbin. Es unterstützt ACL, RBAC, ABAC und RESTful-Zugriffskontrollmodelle.
-
Casdoor provides phone verification codes, email verification codes, and password retrieval functionality.
-
Casdoor supports auditing and recording of access logs.
-
Casdoor integrates with Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, and Qiniu Cloud for image CDN and cloud storage.
-
Casdoor ermöglicht die Anpassung von Registrierungs-, Anmelde- und Passwortwiederherstellungsseiten.
-
Casdoor supports integration with existing systems through database synchronization, enabling a smooth transition to Casdoor.
-
Casdoor supports mainstream databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server, and supports extending to new databases with plugins.
Wie es funktioniert

Schritt 0 (Vorwissen)
- Casdoor uses OAuth 2.0 for authorization. For a short intro to OAuth 2.0, see An introduction to OAuth 2.
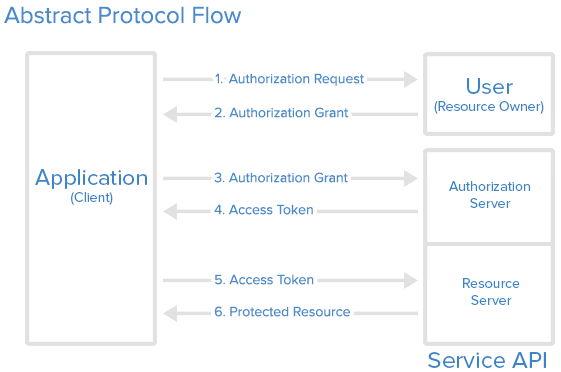
Schritt 1 (Autorisierungsanfrage)
Ihre Anwendung (die eine Website oder eine andere Anwendung sein könnte) sollte eine URL im folgenden Format zusammenstellen: endpoint/login/oauth/authorize?client_id=xxx&response_type=code&redirect_uri=xxx&scope=read&state=xxx. Replace endpoint with your Casdoor host URL and xxx with your own information.
Wie füllt man die xxx Teile aus?
- client_id: From the Application settings in Casdoor.
- redirect_uri: Your application’s callback URL; Casdoor redirects here after authorization.
- state: Your application name (or any value you use to correlate the request).
Die Anwendung wird den Benutzer auffordern: "Hey, ich brauche einige Ressourcen und ich benötige deine Erlaubnis, um auf diese Ressourcen zuzugreifen. Kannst du zu dieser URL gehen und deinen Benutzernamen und dein Passwort für mich eingeben?" Mit der korrekt zusammengesetzten URL wird Ihre Anwendung den Benutzer dazu bringen, eine Anfrage an diese URL zu stellen, und die Autorisierungsanfrage ist abgeschlossen.
Dieser Schritt ist unkompliziert: Der Benutzer wird zur in Schritt 1 zusammengesetzten URL umgeleitet, und der Benutzer wird die Anmeldeseite von Casdoor sehen.
Schritt 2 (Autorisierungszuschlag)
Indem der Benutzer den richtigen Benutzernamen und die Anmeldeinformationen auf der Anmeldeseite eingibt, weiß Casdoor nun die Identität des Benutzers und steht kurz davor, zwei Informationen zurück an die in Schritt 1 festgelegte Callback-URL zu senden: code und state. Mit diesen beiden Informationen, die an Ihre Anwendung zurückgesendet werden, wird die Autorisierung der App gewährt und der Autorisierungszuschlag ist abgeschlossen.
The user opens the URL and provides credentials to Casdoor. Casdoor will say: "Looking good ~ this is the user (who is authorizing the Application to receive the code and state) I know in my database, and I will send the code and state back to the Application using the callback URL (redirect_uri)".
Casdoor bietet auch Drittanbieter-Logins an.
In diesem Fall sehen Sie anstelle der Seite zur Eingabe der Anmeldeinformationen eine Liste von Drittanbieter-Anbietern. Sie können sich mit diesen Anbietern bei Ihrer App anmelden, wobei Casdoor als Zwischenschicht (Middleware) fungiert. You can log in to your app using these providers, with Casdoor acting as middleware.
Schritt 3 (Autorisierungszuschlag)
Casdoor antwortet Ihrer Anwendung: "Weißt du was, dieser code scheint legitim zu sein. Du musst die richtige Anwendung sein. Hier ist das access_token für dich." Mit diesem code bestätigt Casdoor, dass es sich um eine autorisierte Anwendung handelt (autorisiert vom richtigen Benutzer in Schritt 2), die versucht, das access_token zu erhalten (das später verwendet wird, um auf mehr Ressourcen zuzugreifen). In diesem Schritt sagt Ihre Anwendung: "Super! Ich habe gerade das frische und leckere access_token erhalten. Jetzt kann ich es verwenden, um auf etwas Wertvolleres vom Resource Server zuzugreifen!"
Schritt 4 (Zugriffstoken)
Ihre Anwendung wendet sich dann an den Resource Server und sagt: "Hey Kumpel, kannst du dir dieses access_token ansehen? Ich habe es von Casdoor erhalten. Möchtest du überprüfen, ob dies das richtige Token ist, das du Casdoor ausgestellt hast?" You must be the authorized Application. Und das ist im Grunde, wie Casdoor mit Ihrer Anwendung funktioniert.
Schritt 5 (Zugriffstoken)
Casdoor kann sowohl als Autorisierungsserver als auch als Ressourcenserver agieren. I just got the fresh access_token. Casbin-OA ist eine der Casbin-Webanwendungen.
Es verwendet Casdoor zur Authentifizierung. Casnode ist das offizielle Forum, das von der Casbin-Community entwickelt wurde. Es verwendet Casdoor als Authentifizierungsplattform und verwaltet Mitglieder.
Schritt 6 (Geschützte Ressource)
Casdoor besteht aus zwei Teilen: Casdoor wird sagen: "Sieht gut aus ~ das ist der Benutzer (der die Anwendung autorisiert, den code und state zu erhalten), den ich in meiner Datenbank kenne, und ich werde den code und state zurück an die Anwendung senden, indem ich die Callback-URL (redirect_uri) verwende". https://github.com/casdoor/casdoor/tree/master/web
https://github.com/casdoor/casdoor
Casdoor ist eine UI-first Identity Access Management (IAM) / Single-Sign-On (SSO) Plattform mit Web-UI, die OAuth 2.0, OIDC, SAML, CAS, LDAP, SCIM, WebAuthn, TOTP, MFA, RADIUS, Google Workspace, Active Directory und Kerberos unterstützt. In anderen Worten, Casdoor autorisiert Ihre Anwendung, auf Ressourcen zuzugreifen, üblicherweise die Informationen des aktuell eingeloggten Benutzers, aus Casdoors Datenbank.
Online-Demo
Casdoor
Hier ist eine von Casbin bereitgestellte Online-Demo.
Globaler Admin-Login:
- Benutzername:
admin - Passwort:
123
Casbin-OA
Casbin-OA ist eine der Casbin Web-Apps. Es verwendet Casdoor zur Authentifizierung.
- Casbin-OA
- Source code:
https://github.com/casbin/casbin-oa
Casnode
Casnode ist das offizielle Forum, entwickelt von der Casbin-Community.
Es verwendet Casdoor als Authentifizierungsplattform und verwaltet Mitglieder.
- Casnode
- Source code:
https://github.com/casbin/casnode
Architektur
Casdoor besteht aus zwei Teilen:
| Name | Beschreibung | Sprache | Quellcode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontend | Web-Frontend-UI für Casdoor | JavaScript + React | https://github.com/casdoor/casdoor/tree/master/web |
| Backend | RESTful API-Backend für Casdoor | Golang + Beego + SQL | https://github.com/casdoor/casdoor |