Berechtigungskonfiguration
This page explains each field in the Edit Permission page where you configure permission policies for your organization.
Accessing the Permission Configuration
To access the permission configuration page:
- Log in to your Casdoor instance
- Navigate to Permissions in the sidebar
- Click Add to create a new permission or click on an existing permission to edit it
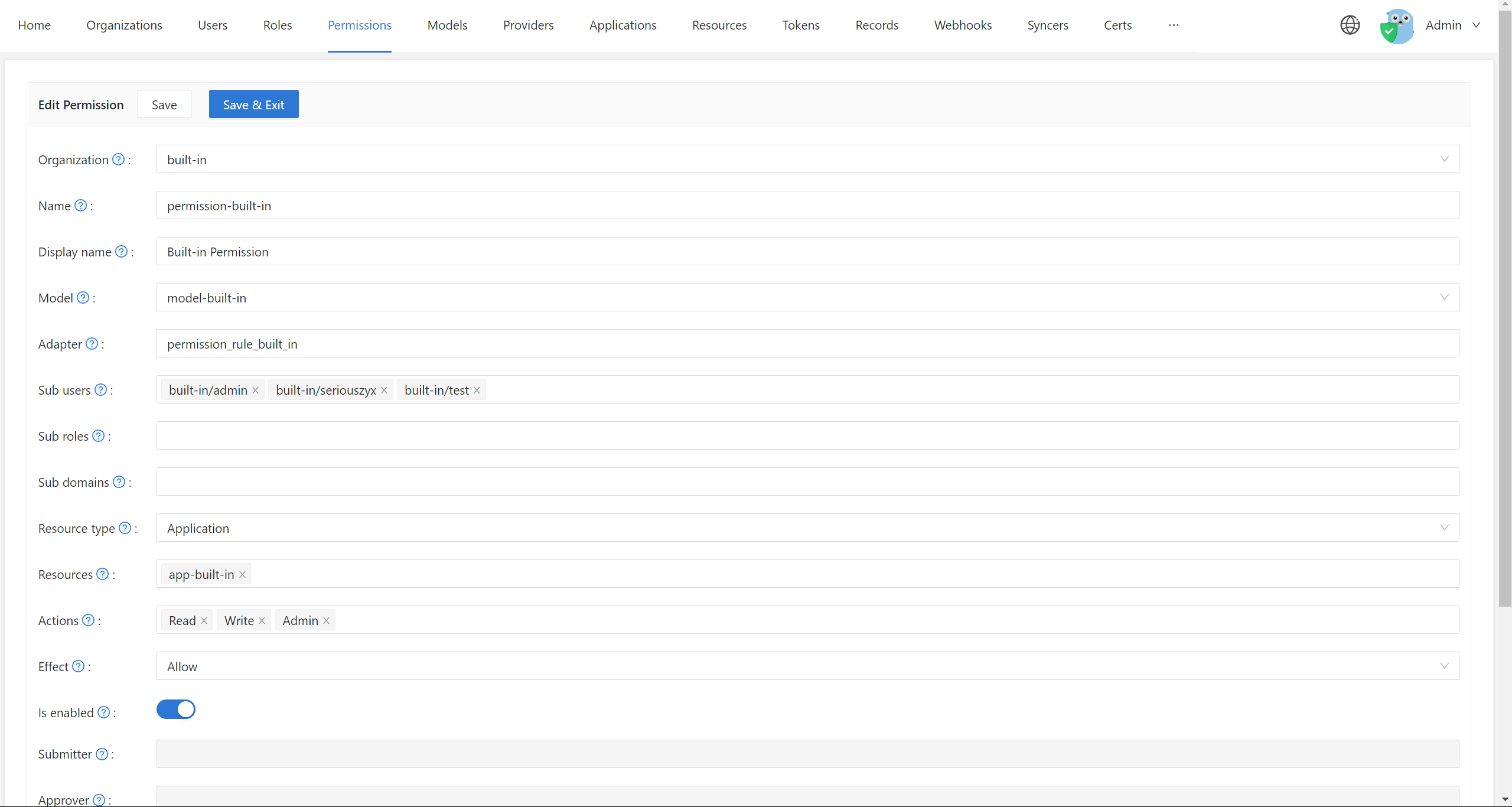
Configuration Fields
Basic Information
Organization
The name of the organization to which the policy belongs. Eine Organisation kann mehrere Berechtigungsrichtliniendateien haben. You can select the organization from the dropdown menu in the Edit Permission page.
Name
The globally unique name of the permission policy in the organization. Er wird verwendet, um die Richtliniendatei zu identifizieren.
- Must be unique within the organization
- Used as the identifier when calling Casbin APIs
Display name
A user-friendly name for the permission policy. This is shown in the Casdoor Web UI for better readability.
Model and Storage Configuration
Model
The name of the model file that describes the structure and matching patterns of the permission policy. You can configure models in the Edit Model page.
Models define how permission checks are performed. For example:
- Simple ACL (Access Control List)
- RBAC (Role-Based Access Control)
- ABAC (Attribute-Based Access Control)
Learn more about models in the Casbin documentation.
Use the Casbin Online Editor to create and test your model before adding it to Casdoor.
Adapter
This field specifies the database table name where the permission policy rules are stored.
Casdoor uses its own database to store permission policies:
- If this field is empty, the permission policy will be stored in the
permission_ruletable - If specified, it will be stored in the specified database table
- If the specified table name does not exist in the database, it will be created automatically
Important
Each Model should use a separate Adapter (table name). Different models with different structures should not share the same table, as this may cause conflicts when loading policies.
Learn more about adapters in the Adapter documentation.
Adapter and Model relationship
In Casdoor, adapters are not configured per Permission.
The adapter and authorization behavior (such as RBAC or ABAC support) are defined at the Model level. A Permission only references a selected Model and provides policy data (subjects, resources, actions, effects).
If RBAC-related fields (for example, Sub-users or Sub-roles) are disabled on the Permission page, it means the selected Model does not define a role_definition or does not support RBAC.
To use an adapter with a Permission:
- Create or edit a Model and configure it with the appropriate Casbin definition and adapter.
- Save the Model.
- Select this Model when creating or editing a Permission.
This behavior is expected and by design.
Subject Configuration
These fields define who the permission policy applies to.
Sub users
Which users will the permission policy be applied to. You can select specific users from the Edit Permission page.
Examples:
- Select specific users like
alice,bob - Leave empty to not restrict by user
Sub roles
If the RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) model is used, you can select which roles will be applied to the permission policy. You configure roles in the Edit Role page.
This will add permission policies such as g, user, role for every user in this role.
Examples:
- Select roles like
admin,editor,viewer - All users with these roles will inherit the permissions
Role-Based Permissions
Using roles is a powerful way to manage permissions at scale. Instead of assigning permissions to individual users, you assign them to roles, and then assign roles to users.
Sub domains
Which domains will the permission policy be applied to. This is useful for multi-tenant scenarios.
Examples:
domain1,domain2- Leave empty if not using domain-based access control
Object and Action Configuration
These fields define what resources and what actions are controlled by the policy.
Resource type
In the current version, Casdoor does not use this field for external applications that want to authenticate. You can ignore it for now or use it for your own categorization purposes.
Resources
This field describes the resources for which you wish to enforce permission control.
Note that the resources here are not those configured in the Resources page of the Casdoor Web UI. You can add any string you want here, such as:
- A URL:
/api/users,/admin/dashboard - A file name:
document.pdf,config.yaml - A resource identifier:
project:123,database:users
You can add multiple resources, and Casdoor will create permission rules for each combination of resource and action.
Actions
This field describes the actions to operate on resources. Similar to resources, it can be any string you want, such as:
- HTTP methods:
GET,POST,PUT,DELETE - CRUD operations:
read,write,update,delete - Custom actions:
view,edit,approve,publish
Please note that Casdoor will convert all these strings to lowercase before storing them. Additionally, Casdoor will apply all actions to each resource. You cannot specify that an action only takes effect on certain resources in this configuration page.
If you need fine-grained control over action-resource combinations, you should define this in your Model file.
Effect Configuration
Effect
This option takes effect for Casdoor itself to control application access.
If you want an external application to enforce permission controls using the interface Casdoor exposes, this field won't do anything. You should describe the effect of pattern matching in the Model file using allow or deny rules.
Example Configuration
As you can see, this configuration page is almost tailor-made for the (sub, obj, act) model, which is one of the most common permission models.
Here's an example configuration:
- Model:
rbac_model(Role-Based Access Control) - Sub roles:
admin,editor - Resources:
/api/users,/api/posts - Actions:
read,write
This would allow users with the admin or editor role to perform read and write actions on the /api/users and /api/posts resources.
Related Topics
- Permission Overview: Understand the basics of permissions in Casdoor
- Exposed Casbin APIs: Use permissions in your external applications
- Adapters: Configure policy storage adapters
- Account Customization: Configure View rule and Modify rule for user account fields
- User Roles: Manage user roles in the Edit Role page