Overview
Certificates (Certs) in Casdoor are used for signing and verifying tokens, as well as for securing communications in various integrations. They contain cryptographic keys that are essential for authentication and encryption processes.
Certificate Properties
Each certificate in Casdoor has the following properties:
- Owner: The organization that owns the certificate
- Name: The unique name of the certificate
- CreatedTime: When the certificate was created
- DisplayName: A human-readable name for the certificate
- Scope: The scope of the certificate (e.g.,
JWT,SAML,Payment) - Type: The type of certificate (e.g.,
x509,Payment) - CryptoAlgorithm: The cryptographic algorithm used (e.g.,
RS256for RSA,ES256for ECDSA) - BitSize: The key size in bits (e.g., 2048, 4096)
- ExpireInYears: The expiration period of the certificate in years
- Certificate: The public certificate content
- PrivateKey: The private key content (stored securely)
Certificate Scopes
Certificates in Casdoor serve different purposes based on their scope:
JWT Certificates
JWT certificates are used to sign and verify JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for authentication. When a user logs in through Casdoor, the access token is signed using the private key of the JWT certificate.
Casdoor supports both RSA and ECDSA signing algorithms for JWT tokens. While RSA (RS256, RS384, RS512) has been the traditional choice, ECDSA algorithms (ES256, ES384, ES512) offer smaller signature sizes and faster signature verification with equivalent security levels. This is particularly beneficial when you need to reduce token size for mobile applications or improve performance in high-throughput scenarios.
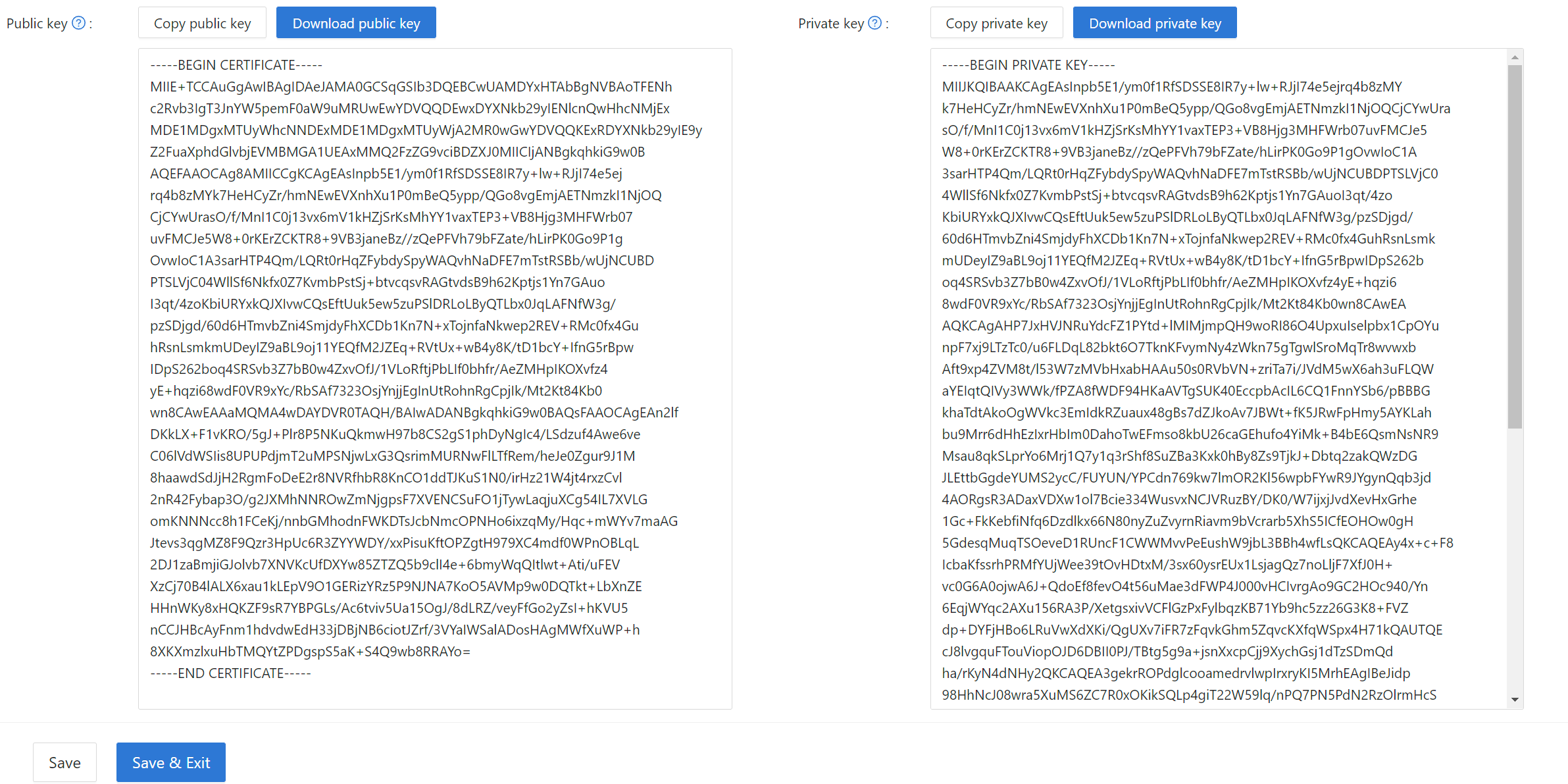
When configuring JWT certificates, you can choose between RSA and ECDSA based on your security requirements and compatibility needs. The JWT public key is required when configuring Casdoor SDK in your application. You can find and download the public key from the certificate edit page.
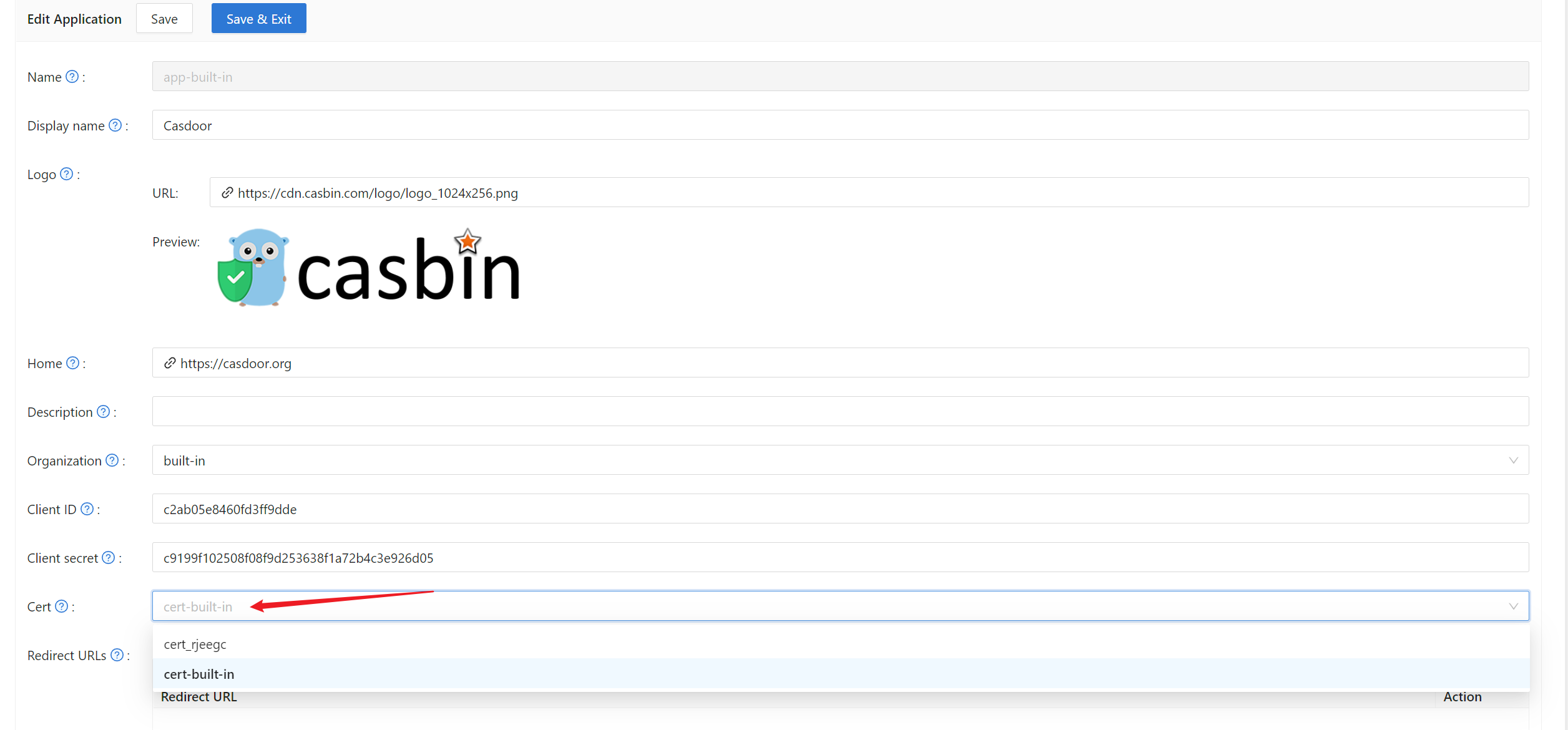
Once you have created a JWT certificate, you can select it in your application settings:
SAML Certificates
SAML certificates are used for signing and encrypting SAML assertions in Single Sign-On (SSO) integrations.
Use cases:
- SAML-based SSO integrations
- Signing SAML responses
- Encrypting SAML assertions for security
When configuring SAML, you need to create certificates for both the Identity Provider (IdP) and Service Provider (SP) to ensure secure communication.
For more information about SAML configuration, see the SAML documentation.
Payment Certificates
Payment certificates are used to secure payment transactions with payment providers like Alipay and WeChat Pay.
Use cases:
- Securing API communications with payment gateways
- Signing payment requests
- Verifying payment callbacks
For example, when integrating with Alipay, you need to create certificates for:
- App Cert: Contains the application's public certificate and private key
- Root Cert: Contains the payment provider's certificates
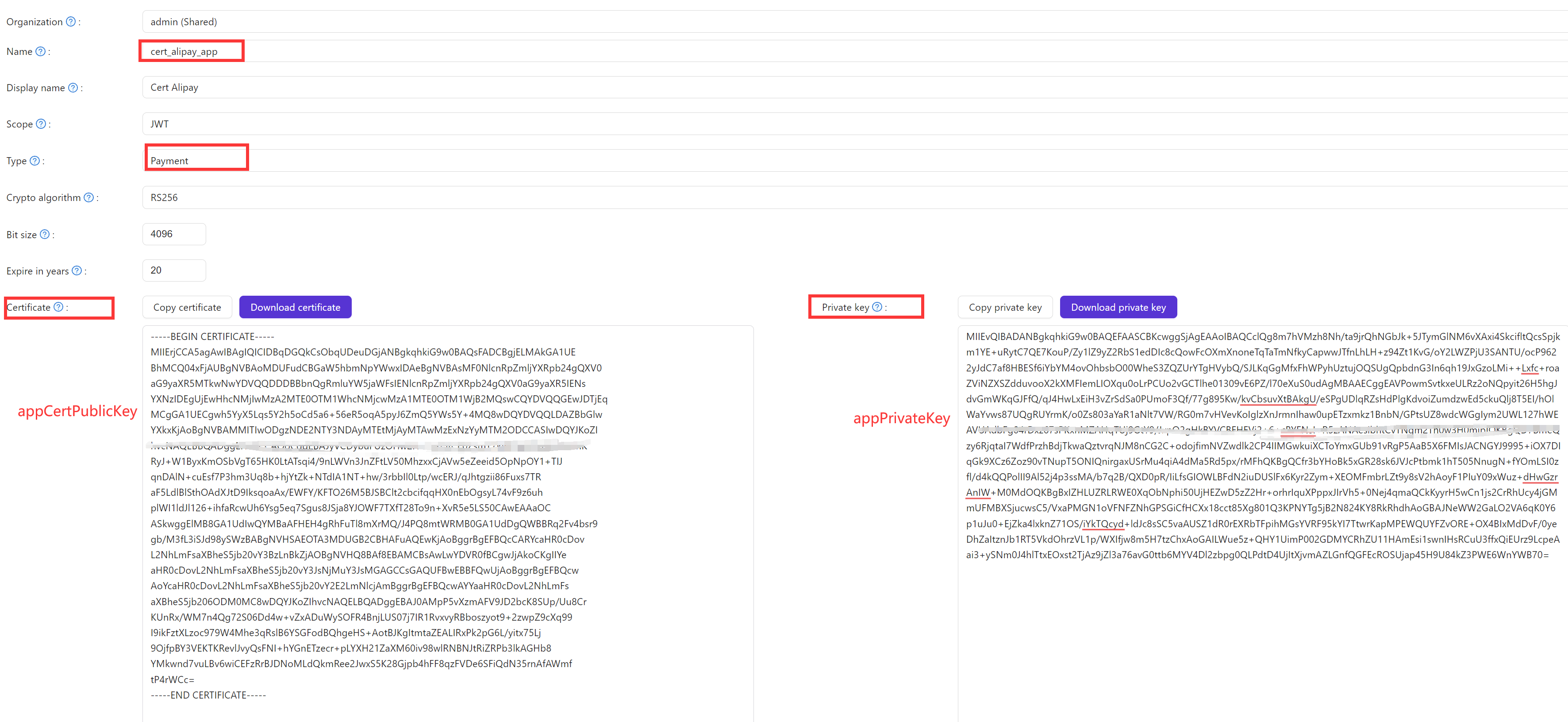
For more details, refer to the Alipay Payment Provider and WeChat Pay Provider documentation.
Creating a Certificate
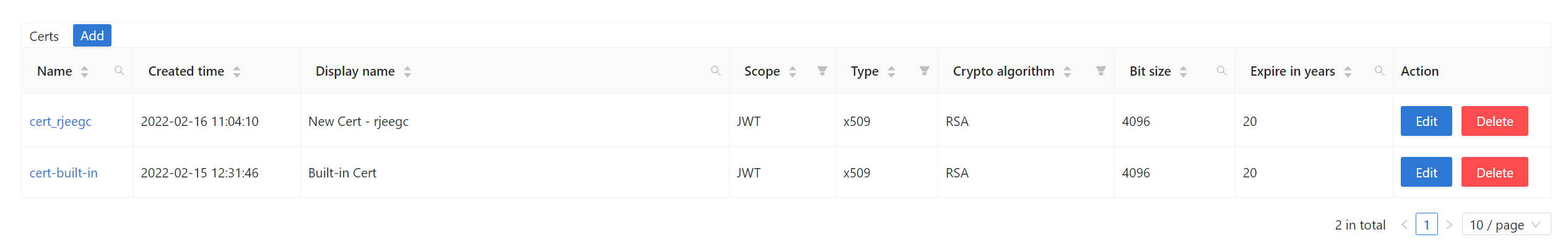
To create a new certificate in Casdoor:
- Navigate to the Certs page in the Casdoor admin console
- Click the Add button to create a new certificate
- Fill in the required fields:
- Name: A unique identifier for the certificate
- Display Name: A human-readable name
- Scope: Select the appropriate scope (JWT, SAML, Payment)
- Type: Select the certificate type
- Crypto Algorithm: Choose the cryptographic algorithm (e.g., RS256 for RSA, ES256 for ECDSA). For JWT certificates, both RSA and ECDSA algorithms are supported
- Bit Size: Set the key size (typically 2048 or 4096 bits)
- Expire In Years: Set the expiration period
- You can either:
- Generate a new certificate automatically by saving the form
- Upload an existing certificate and private key
Using Certificates
In Applications
After creating a JWT certificate, you need to associate it with your application:
- Go to the Applications page
- Edit your application
- In the Cert field, select the certificate you created
- Save the application
The certificate will now be used to sign all tokens issued by that application.
In SDK Configuration
When configuring Casdoor SDK in your backend application, you need to provide the public key from the JWT certificate:
var CasdoorEndpoint = "https://door.casdoor.com"
var ClientId = "541738959670d221d59d"
var ClientSecret = "66863369a64a5863827cf949bab70ed560ba24bf"
var CasdoorOrganization = "casbin"
var CasdoorApplication = "app-casnode"
//go:embed token_jwt_key.pem
var JwtPublicKey string
func init() {
auth.InitConfig(CasdoorEndpoint, ClientId, ClientSecret, JwtPublicKey, CasdoorOrganization, CasdoorApplication)
}
You can download the public key from the certificate edit page in Casdoor.
For more information about SDK configuration, see the SDK documentation.
In Payment Providers
When setting up payment providers, you need to configure the appropriate certificates:
- Create the required certificates (e.g., App Cert and Root Cert for Alipay)
- Go to the Providers page
- Edit or create your payment provider
- In the Cert field, select the certificate you created
- Save the provider
Best Practices
- Key Size: Use at least 2048-bit keys for RSA certificates. For higher security, consider 4096-bit keys.
- Expiration: Set appropriate expiration periods. For production environments, 1-5 years is typical.
- Security: Keep private keys secure and never expose them in client-side code or public repositories.
- Rotation: Regularly rotate certificates before they expire to maintain security.
- Backup: Keep secure backups of your certificates and private keys.
- Separate Certificates: Use different certificates for different purposes (JWT, SAML, Payment) to limit the impact of potential key compromise.
Certificate Management
You can manage certificates through:
- Web UI: The Casdoor admin console provides a user-friendly interface for certificate management
- API: Use the Casdoor REST API to programmatically manage certificates
- Data Initialization: Certificates can be included in initialization files for automated deployments
For more information about data initialization, see the Data Initialization documentation.