Casdoor SDKs
Introduction
Compared to the standard OIDC protocol, Casdoor's SDK provides additional functionality, such as user management and resource uploading. Connecting to Casdoor via the Casdoor SDK requires more time than using a standard OIDC client library but provides the best flexibility and the most powerful API.
Casdoor SDKs can be divided into two categories:
- Frontend SDK: SDKs for websites (like Javascript SDK, Vue SDK) and mobile apps (Android or iOS SDKs). Casdoor supports providing authentication for both websites and mobile applications.
- Backend SDK: SDKs for backend languages like Go, Java, Node.js, Python, PHP, etc.
If your website is developed with a frontend-backend separation architecture, you can use the Javascript
SDK: casdoor-js-sdk, React SDK: casdoor-react-sdk, or Vue SDK: casdoor-vue-sdk to integrate Casdoor in the frontend. If your web application is a traditional website developed with JSP or PHP, you can use backend SDKs only. See an example: casdoor-python-vue-sdk-example
| Mobile SDK | Description | SDK code | Example code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android SDK | For Android apps | casdoor-android-sdk | casdoor-android-example |
| iOS SDK | For iOS apps | casdoor-ios-sdk | casdoor-ios-example |
| React Native SDK | For React Native apps | casdoor-react-native-sdk | casdoor-react-native-example |
| Flutter SDK | For Flutter apps | casdoor-flutter-sdk | casdoor-flutter-example |
| Firebase SDK | For Google Firebase apps | casdoor-firebase-example | |
| Unity Games SDK | For Unity 2D/3D PC/Mobile games | casdoor-dotnet-sdk | casdoor-unity-example |
| uni-app SDK | For uni-app apps | casdoor-uniapp-sdk | casdoor-uniapp-example |
| Desktop SDK | Description | SDK code | Example code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electron SDK | For Electron apps | casdoor-js-sdk | casdoor-electron-example |
| .NET Desktop SDK | For .NET desktop apps | casdoor-dotnet-sdk | WPF: casdoor-dotnet-desktop-example WinForms: casdoor-dotnet-winform-example Avalonia UI: casdoor-dotnet-avalonia-example |
| C/C++ SDK | For C/C++ desktop apps | casdoor-cpp-sdk | casdoor-cpp-qt-example |
| Web frontend SDK | Description | SDK code | Example code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Javascript SDK | For traditional non-SPA websites | casdoor-js-sdk | Nodejs backend: casdoor-raw-js-example Go backend: casdoor-go-react-sdk-example |
| Frontend-only SDK | For frontend-only SPA websites | casdoor-js-sdk | casdoor-react-only-example |
| React SDK | For React websites | casdoor-react-sdk | Nodejs backend: casdoor-nodejs-react-example Java backend: casdoor-spring-security-react-example |
| Next.js SDK | For Next.js websites | nextjs-auth | |
| Nuxt SDK | For Nuxt websites | nuxt-auth | |
| Vue SDK | For Vue websites | casdoor-vue-sdk | casdoor-python-vue-sdk-example |
| Angular SDK | For Angular websites | casdoor-angular-sdk | casdoor-nodejs-angular-example |
| Flutter SDK | For Flutter Web websites | casdoor-flutter-sdk | casdoor-flutter-example |
| ASP.NET SDK | For ASP.NET Blazor WASM websites | Blazor.BFF.OpenIDConnect.Template | casdoor-dotnet-blazorwasm-oidc-example |
| Firebase SDK | For Google Firebase apps | casdoor-firebase-example |
Next, use one of the following backend SDKs based on the language of your backend:
| Web backend SDK | Description | Sdk code | Example code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Go SDK | For Go backends | casdoor-go-sdk | casdoor-go-react-sdk-example |
| Java SDK | For Java backends | casdoor-java-sdk | casdoor-spring-boot-starter, casdoor-spring-boot-example, casdoor-spring-security-react-example |
| Node.js SDK | For Node.js backends | casdoor-nodejs-sdk | casdoor-nodejs-react-example |
| Python SDK | For Python backends | casdoor-python-sdk | Flask: casdoor-python-vue-sdk-example Django: casdoor-django-js-sdk-example FastAPI: casdoor-fastapi-js-sdk-example |
| PHP SDK | For PHP backends | casdoor-php-sdk | wordpress-casdoor-plugin |
| .NET SDK | For ASP.NET backends | casdoor-dotnet-sdk | casdoor-dotnet-sdk-example |
| Rust SDK | For Rust backends | casdoor-rust-sdk | casdoor-rust-example |
| C/C++ SDK | For C/C++ backends | casdoor-cpp-sdk | casdoor-cpp-qt-example |
| Dart SDK | For Dart backends | casdoor-dart-sdk | |
| Ruby SDK | For Ruby backends | casdoor-ruby-sdk |
For a full list of the official Casdoor SDKs, please see: https://github.com/orgs/casdoor/repositories?q=sdk&type=all&language=&sort=
How to use Casdoor SDK?
1. Backend SDK configuration
When your application starts up, you need to initialize the Casdoor SDK configuration by calling the InitConfig() function with the required parameters. Using casdoor-go-sdk as an
example: https://github.com/casbin/casnode/blob/6d4c55f5c9a3c4bd8c85f2493abad3553b9c7ac0/controllers/account.go#L51-L64
var CasdoorEndpoint = "https://door.casdoor.com"
var ClientId = "541738959670d221d59d"
var ClientSecret = "66863369a64a5863827cf949bab70ed560ba24bf"
var CasdoorOrganization = "casbin"
var CasdoorApplication = "app-casnode"
//go:embed token_jwt_key.pem
var JwtPublicKey string
func init() {
auth.InitConfig(CasdoorEndpoint, ClientId, ClientSecret, JwtPublicKey, CasdoorOrganization, CasdoorApplication)
}
All the parameters for InitConfig() are explained as follows:
| Parameter | Must | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | Yes | Casdoor Server URL, like https://door.casdoor.com or http://localhost:8000 |
| clientId | Yes | Client ID for the Casdoor application |
| clientSecret | Yes | Client secret for the Casdoor application |
| jwtPublicKey | Yes | The public key for the Casdoor application's cert |
| organizationName | Yes | The name for the Casdoor organization |
| applicationName | No | The name for the Casdoor application |
The jwtPublicKey can be managed in the Certs page as below.
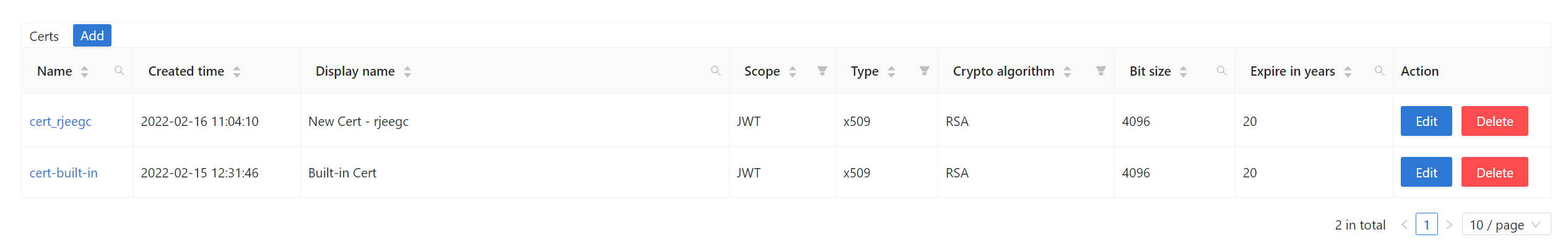
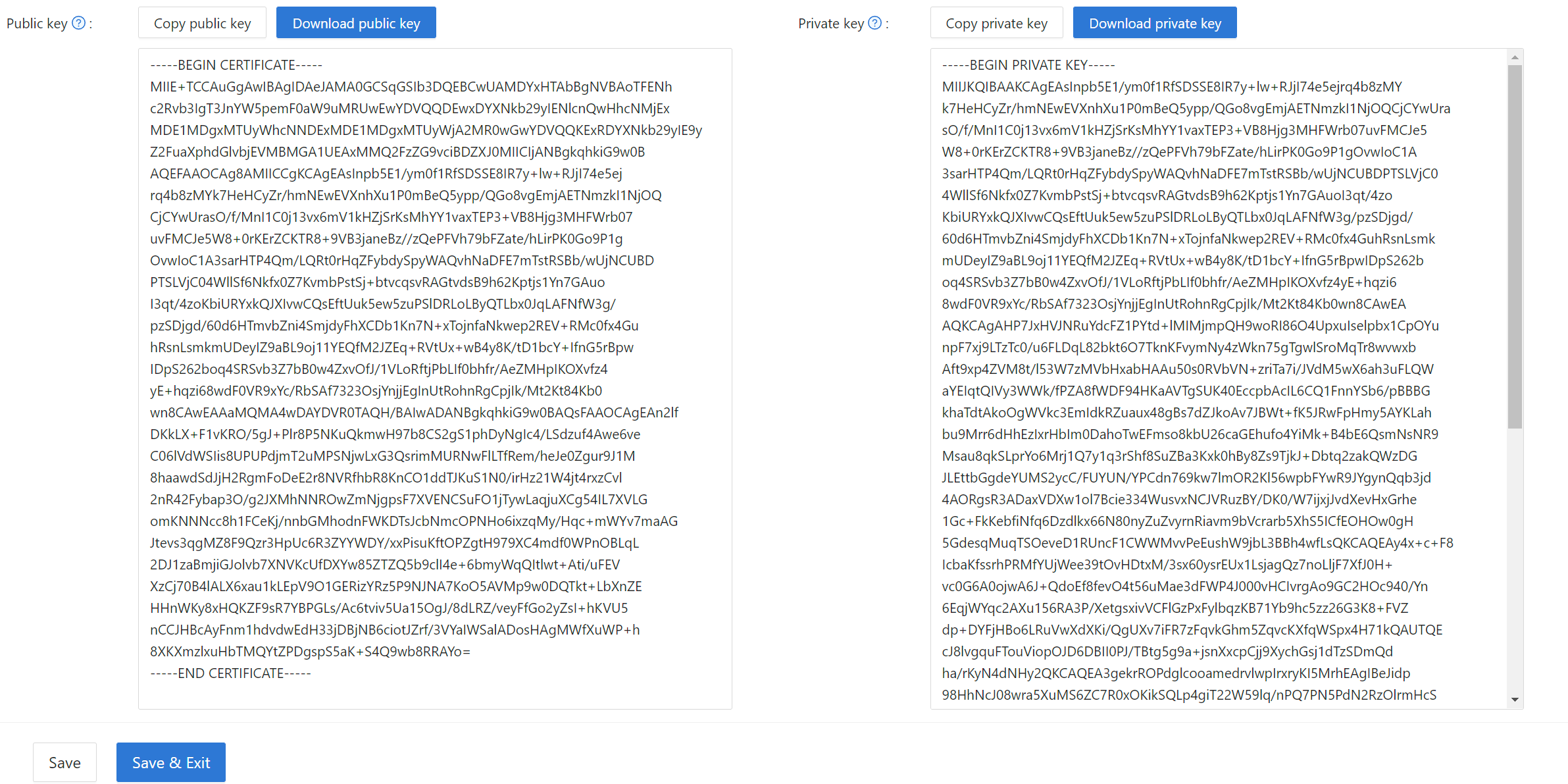
You can find the public key in the cert edit page, copy it or download it for the sdk.
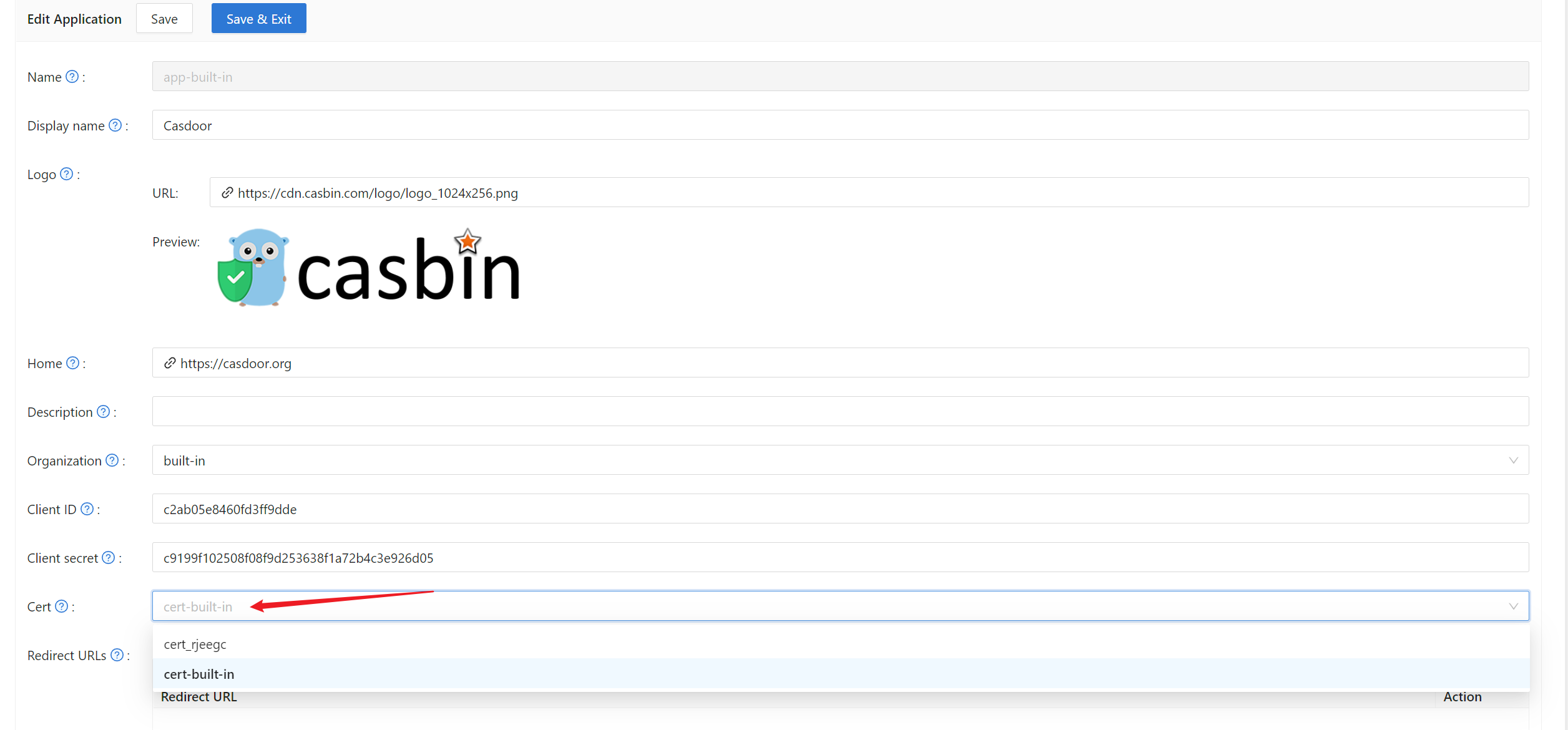
Then you can select the cert in the application edit page.
2. Frontend configuration
First, install casdoor-js-sdk via NPM or Yarn:
npm install casdoor-js-sdk
Or:
yarn add casdoor-js-sdk
Then define the following utility functions (better in a global JS file like Setting.js):
import Sdk from "casdoor-js-sdk";
export function initCasdoorSdk(config) {
CasdoorSdk = new Sdk(config);
}
export function getSignupUrl() {
return CasdoorSdk.getSignupUrl();
}
export function getSigninUrl() {
return CasdoorSdk.getSigninUrl();
}
export function getUserProfileUrl(userName, account) {
return CasdoorSdk.getUserProfileUrl(userName, account);
}
export function getMyProfileUrl(account) {
return CasdoorSdk.getMyProfileUrl(account);
}
export function getMyResourcesUrl(account) {
return CasdoorSdk.getMyProfileUrl(account).replace("/account?", "/resources?");
}
export function signin() {
return CasdoorSdk.signin(ServerUrl);
}
export function showMessage(type, text) {
if (type === "") {
return;
} else if (type === "success") {
message.success(text);
} else if (type === "error") {
message.error(text);
}
}
export function goToLink(link) {
window.location.href = link;
}
In the entrance file of your frontend code (like index.js or app.js in React), you need to initialize
the casdoor-js-sdk by calling the InitConfig() function with required parameters. The first 4 parameters should use the same value as the Casdoor backend SDK. The last parameter redirectPath is relative path for the redirected URL, returned from Casdoor's login page.
const config = {
serverUrl: "https://door.casdoor.com",
clientId: "014ae4bd048734ca2dea",
organizationName: "casbin",
appName: "app-casnode",
redirectPath: "/callback",
};
xxx.initCasdoorSdk(config);
(Optional) Because we are using React as example, our /callback path is hitting the React route. We use the following React component to receive the /callback call and send to the backend. You can ignore this step if you are redirecting to backend directly (like in JSP or PHP).
import React from "react";
import {Button, Result, Spin} from "antd";
import {withRouter} from "react-router-dom";
import * as Setting from "./Setting";
class AuthCallback extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
classes: props,
msg: null,
};
}
componentWillMount() {
this.login();
}
login() {
Setting.signin().then((res) => {
if (res.status === "ok") {
Setting.showMessage("success", `Logged in successfully`);
Setting.goToLink("/");
} else {
this.setState({
msg: res.msg,
});
}
});
}
render() {
return (
<div style={{textAlign: "center"}}>
{this.state.msg === null ? (
<Spin
size="large"
tip="Signing in..."
style={{paddingTop: "10%"}}
/>
) : (
<div style={{display: "inline"}}>
<Result
status="error"
title="Login Error"
subTitle={this.state.msg}
extra={[
<Button type="primary" key="details">
Details
</Button>,
<Button key="help">Help</Button>,
]}
/>
</div>
)}
</div>
);
}
}
export default withRouter(AuthCallback);
3. Get login URLs
Next you can show the "Sign up" and "Sign in" buttons or links to your users. The URLs can either be retrieved in the frontend or backend. See more details at: /docs/basic/core-concepts#login-urls
4. Get and verify access token
Here are the steps:
- The user clicks the login URL and is redirected to Casdoor's login page,
like:
https://door.casdoor.com/login/oauth/authorize?client_id=014ae4bd048734ca2dea&response_type=code&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fforum.casbin.com%2Fcallback&scope=read&state=app-casnode - The user enters username & password and clicks
Sign In(or just click the third-party login button likeSign in with GitHub). - The user is redirected back to your application with the authorization code issued by Casdoor (
like:
https://forum.casbin.com?code=xxx&state=yyy), your application's backend needs to exchange the authorization code with the access token and verify that the access token is valid and issued by Casdoor. The functionsGetOAuthToken()andParseJwtToken()are provided by Casdoor backend SDK.
The following code shows how to get and verify the access token. For a real example of Casnode (a forum website written in Go), see: https://github.com/casbin/casnode/blob/6d4c55f5c9a3c4bd8c85f2493abad3553b9c7ac0/controllers/account.go#L51-L64
// get code and state from the GET parameters of the redirected URL
code := c.Input().Get("code")
state := c.Input().Get("state")
// exchange the access token with code and state
token, err := auth.GetOAuthToken(code, state)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// verify the access token
claims, err := auth.ParseJwtToken(token.AccessToken)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
If ParseJwtToken() finishes with no error, then the user has successfully logged into the application. The
returned claims can be used to identity the user later.
4. Identify user with access token
This part is actually your application's own business logic and not part of OIDC, OAuth or Casdoor. We just provide good practices as a lot of people don't know what to do for the next step.
In Casdoor, access token is usually identical as ID token. They are the same thing. So the access token contains all information for the logged-in user.
The variable claims returned by ParseJwtToken() is defined as:
type Claims struct {
User
AccessToken string `json:"accessToken"`
jwt.RegisteredClaims
}
User: the User object, containing all information for the logged-in user, see definition at: /docs/basic/core-concepts#userAccessToken: the access token string.jwt.RegisteredClaims: some other values required by JWT.
At this moment, the application usually has two ways to remember the user session: session and JWT.
Session
The Method to set session varies greatly depending on the language and web framework. E.g., Casnode
uses Beego web framework and set session by calling: c.SetSessionUser().
token, err := auth.GetOAuthToken(code, state)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
claims, err := auth.ParseJwtToken(token.AccessToken)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
claims.AccessToken = token.AccessToken
c.SetSessionUser(claims) // set session
JWT
The accessToken returned by Casdoor is actually a JWT. So if your application uses JWT to keep user session, just use the access token directly for it:
- Send the access token to frontend, save it in places like localStorage of the browser.
- Let the browser send the access token to backend for every request.
- Call
ParseJwtToken()or your own function to verify the access token and get logged-in user information in your backend.
5. (Optional) Interact with the User table
This part is provided by Casdoor Public API and not part of the OIDC or OAuth.
Casdoor Backend SDK provides a lot of helper functions, not limited to:
GetUser(name string): get a user by username.GetUsers(): get all users.AddUser(): add a user.UpdateUser(): update a user.DeleteUser(): delete a user.CheckUserPassword(auth.User): check user's password.
These functions are implemented by making RESTful calls against Casdoor Public API. If a function is not provided in Casdoor Backend SDK, you can make RESTful calls by yourself.
6. (Optional) Manage Applications via SDK
Casdoor SDKs also provide functions to manage applications programmatically:
AddApplication(): create a new application.GetApplication(name string): get an application by name.GetApplications(): get all applications.UpdateApplication(): update an application.DeleteApplication(): delete an application.
When creating applications via SDK using AddApplication(), Casdoor automatically initializes essential fields with sensible defaults. This includes signup items (ID, Username, Display name, Password, Confirm password, Email, Phone, Agreement), signin items, and signin methods. This ensures applications created programmatically work correctly in the UI without requiring manual configuration of these basic settings.