SAML IdP overview
Casdoor can act as a SAML 2.0 IdP. This page covers SP configuration, Casdoor IdP settings, and SAML attributes.
Configuration in the SP (service provider)
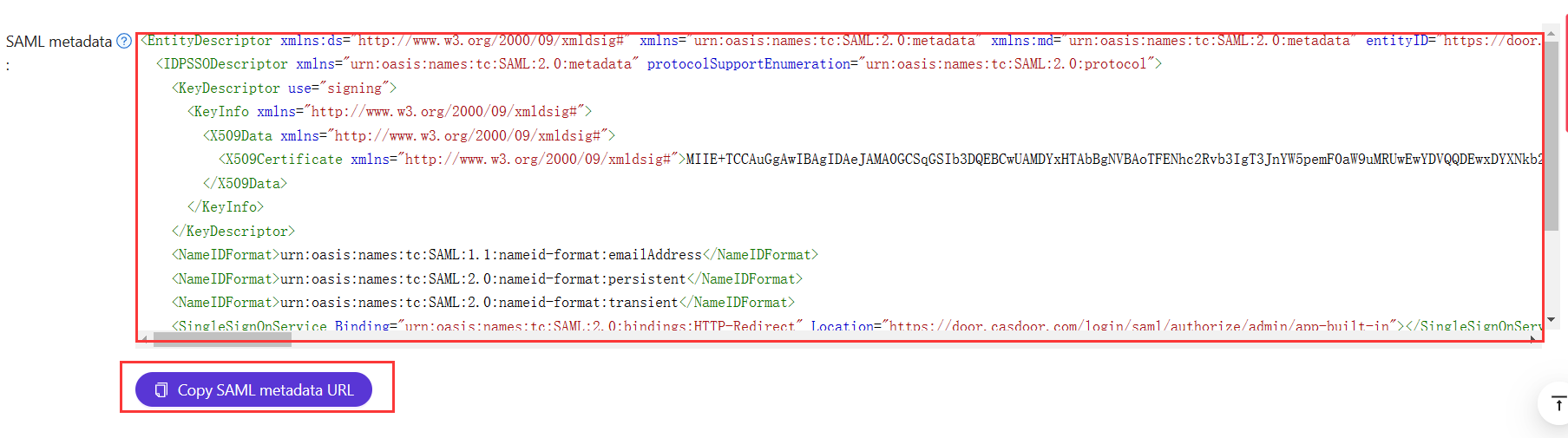
The SP typically needs Single Sign-On URL, Issuer, and Public Certificate. Most SPs can fill these from the Casdoor XML Metadata URL or by uploading the metadata file.
Casdoor metadata URL format: <casdoor-endpoint>/api/saml/metadata?application=admin/<application-name>
Example: if Casdoor is at https://door.casdoor.com and the application is app-built-in:
https://door.casdoor.com/api/saml/metadata?application=admin/app-built-in
The metadata URL is also on the application edit page; copy it and open in a browser to download the XML.
Configuration in Casdoor IdP
Casdoor supports both GET and POST SAMLResponse. Configure the application in Casdoor to match the SAMLResponse binding (GET or POST) that your SP supports.
When integrating Casdoor as a SAML IdP with external identity providers (like Azure AD), the /api/acs endpoint receives SAML responses. This endpoint is configured to accept cross-origin POST requests, allowing IdPs from different domains to send authentication data.
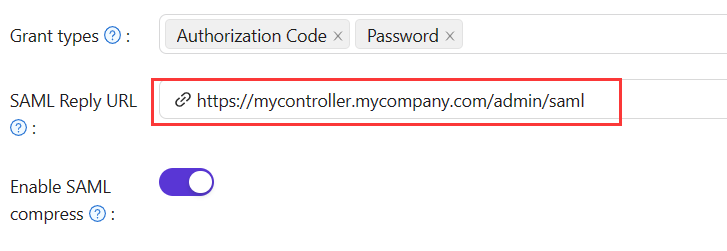
If you fill in the Reply URL, Casdoor will send the SAMLResponse by POST Request. If the Reply URL is empty, Casdoor will use GET request. You might wonder how Casdoor knows the Reply URL of the SP if the Reply URL is empty. Actually, Casdoor can get the URL called AssertionConsumerServiceURL by parsing the SAMLRequest and send the request with SAMLResponse to AssertionConsumerServiceURL. The Reply URL will overwrite the AssertionConsumerServiceURL in SAMLRequest.
-
Reply URL: Type in the URL of the ACS verifying the SAML response.
-
Redirect URL: Type in a unique name. This may be called
AudienceorEntity IDin your SP. Make sure you fill the sameRedirect URLhere as in your SP.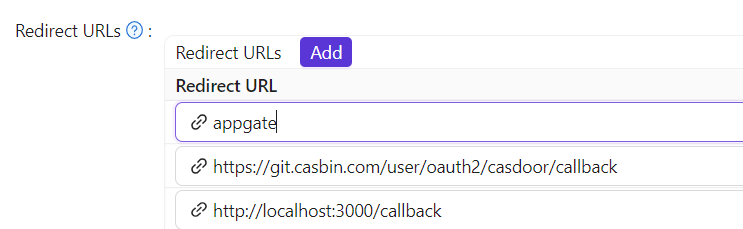
SAML attributes
If the SP requires extra attributes in the SAML response, add them in the SAML attributes table and map user fields as needed.
If the service provider only needs NameID and not extra user attributes (Email, Name, DisplayName, Roles), enable Disable SAML attributes in the application settings. When enabled, Casdoor will omit these attributes from the SAML response, which can help avoid XML namespace issues with certain SPs that have strict validation requirements.
Assertion signature control
SAML responses from Casdoor are always signed to ensure authenticity. However, some service providers may not support or require signed assertions within the response itself. Starting from version 2.81.0, Casdoor added assertion signatures following SAML 2.0 best practices, but this caused compatibility issues with certain SPs like Sentry.
If a service provider does not handle signed assertions correctly, disable assertion signing while keeping the response envelope signed. Toggle the Enable SAML assertion signature option in your application settings to control this behavior. When disabled, Casdoor will sign only the SAML response envelope, which maintains security while ensuring compatibility with a wider range of service providers.
For example
| Name | Name format | Value |
|---|---|---|
https://www.aliyun.com/SAML-Role/Attributes/RoleSessionName | Unspecified | $user.name |
https://www.aliyun.com/SAML-Role/Attributes/Role | Unspecified | acs:ram::1879818006829152:role/$user.roles,acs:ram::1879818006829152:saml-provider/testa |
will generate response with external saml:Attribute
<saml:Attribute Name="https://www.aliyun.com/SAML-Role/Attributes/RoleSessionName" NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:unspecified">
<saml:AttributeValue xsi:type="xs:string">admi122n@outlook.com</saml:AttributeValue>
</saml:Attribute>
<saml:Attribute Name="https://www.aliyun.com/SAML-Role/Attributes/Role" NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:unspecified">
<saml:AttributeValue xsi:type="xs:string"> acs:ram::1879818006829152:role/role1,acs:ram::1879818006829152:saml-provider/testa</saml:AttributeValue>
<saml:AttributeValue xsi:type="xs:string"> acs:ram::1879818006829152:role/role2,acs:ram::1879818006829152:saml-provider/testa</saml:AttributeValue>
</saml:Attribute>
We only support insert $user.owner,$user.name,$user.email,$user.id,$user.phone,$user.roles,$user.permissions,$user.groups
User profile
After successfully logging in, the user profile in the returned SAMLResponse from Casdoor has three fields. The attributes in the XML and the attributes of the user in Casdoor are mapped as follows:
| XML Attribute Name | User field |
|---|---|
| DisplayName | displayName |
| Name | name |
See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SAML_2.0 for more information about SAML and its different versions.
An example
gosaml2 is a SAML 2.0 implementation for Service Providers based on etree and goxmldsig, a pure Go implementation of XML digital signatures. We use this library to test the SAML 2.0 in Casdoor as shown below.
Example: Casdoor at http://localhost:7001/, application app-built-in in org built-in. Add http://localhost:6900/acs/example and http://localhost:6900/saml/acs/example to Redirect URLs in app-built-in.
import (
"crypto/x509"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"io/ioutil"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/xml"
saml2 "github.com/russellhaering/gosaml2"
"github.com/russellhaering/gosaml2/types"
dsig "github.com/russellhaering/goxmldsig"
)
func main() {
res, err := http.Get("http://localhost:7001/api/saml/metadata?application=admin/app-built-in")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
rawMetadata, err := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
metadata := &types.EntityDescriptor{}
err = xml.Unmarshal(rawMetadata, metadata)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
certStore := dsig.MemoryX509CertificateStore{
Roots: []*x509.Certificate{},
}
for _, kd := range metadata.IDPSSODescriptor.KeyDescriptors {
for idx, xcert := range kd.KeyInfo.X509Data.X509Certificates {
if xcert.Data == "" {
panic(fmt.Errorf("metadata certificate(%d) must not be empty", idx))
}
certData, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(xcert.Data)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
idpCert, err := x509.ParseCertificate(certData)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
certStore.Roots = append(certStore.Roots, idpCert)
}
}
randomKeyStore := dsig.RandomKeyStoreForTest()
sp := &saml2.SAMLServiceProvider{
IdentityProviderSSOURL: metadata.IDPSSODescriptor.SingleSignOnServices[0].Location,
IdentityProviderIssuer: metadata.EntityID,
ServiceProviderIssuer: "http://localhost:6900/acs/example",
AssertionConsumerServiceURL: "http://localhost:6900/v1/_saml_callback",
SignAuthnRequests: true,
AudienceURI: "http://localhost:6900/saml/acs/example",
IDPCertificateStore: &certStore,
SPKeyStore: randomKeyStore,
}
http.HandleFunc("/v1/_saml_callback", func(rw http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
err := req.ParseForm()
if err != nil {
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
samlReponse := req.URL.Query().Get("SAMLResponse")
assertionInfo, err := sp.RetrieveAssertionInfo(samlReponse)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)
return
}
fmt.Println(assertionInfo)
if assertionInfo.WarningInfo.InvalidTime {
fmt.Println("here12:", assertionInfo.WarningInfo.InvalidTime)
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)
return
}
if assertionInfo.WarningInfo.NotInAudience {
fmt.Println(assertionInfo)
fmt.Println("here13:", assertionInfo.WarningInfo.NotInAudience)
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)
return
}
fmt.Fprintf(rw, "NameID: %s\n", assertionInfo.NameID)
fmt.Fprintf(rw, "Assertions:\n")
for key, val := range assertionInfo.Values {
fmt.Fprintf(rw, " %s: %+v\n", key, val)
}
fmt.Println(assertionInfo.Values.Get("FirstName"))
fmt.Fprintf(rw, "\n")
fmt.Fprintf(rw, "Warnings:\n")
fmt.Fprintf(rw, "%+v\n", assertionInfo.WarningInfo)
})
println("Visit this URL To Authenticate:")
authURL, err := sp.BuildAuthURL("")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
println(authURL)
println("Supply:")
fmt.Printf(" SP ACS URL : %s\n", sp.AssertionConsumerServiceURL)
err = http.ListenAndServe(":6900", nil)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
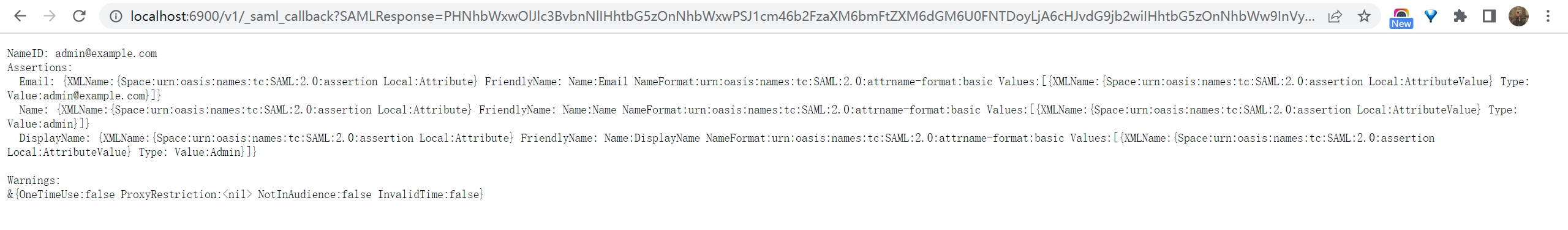
Run the above code, and the console will display the following message.
Visit this URL To Authenticate:
http://localhost:7001/login/saml/authorize/admin/app-built-in?SAMLRequest=lFVbk6K8Fv0rFvNo2QR...
Supply:
SP ACS URL : http://localhost:6900/v1/_saml_callback
Click the URL to authenticate, and the login page of Casdoor will be displayed.

After authentication, the response looks like the examples below.