Kubernetes
According to the Kubernetes documentation, the API Server of Kubernetes can be authenticated using OpenID Connect (OIDC). This article will guide you on how to configure authentication in Kubernetes using Casdoor.
Environment Requirements
Before starting, please make sure that you have the following environment:
- A Kubernetes cluster.
- A Casdoor application like this demo website.
- kubectl command tool (optional).
Kubernetes oidc-issuer-url only accepts URLs which use the https:// prefix.
So your Casdoor application should be deployed on an HTTPS website.
Step 1: Creating a Casdoor App and User Account for Authentication
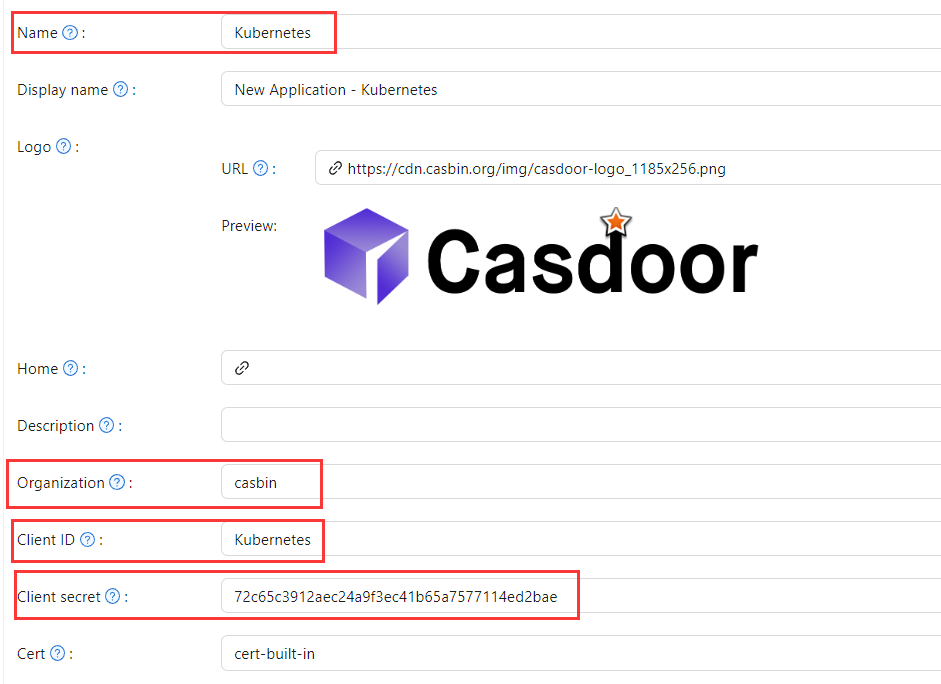
Go to your Casdoor application and add a new application called Kubernetes.
Please remember the Name, Organization, client ID, client Secret, and add some grant types to this app.
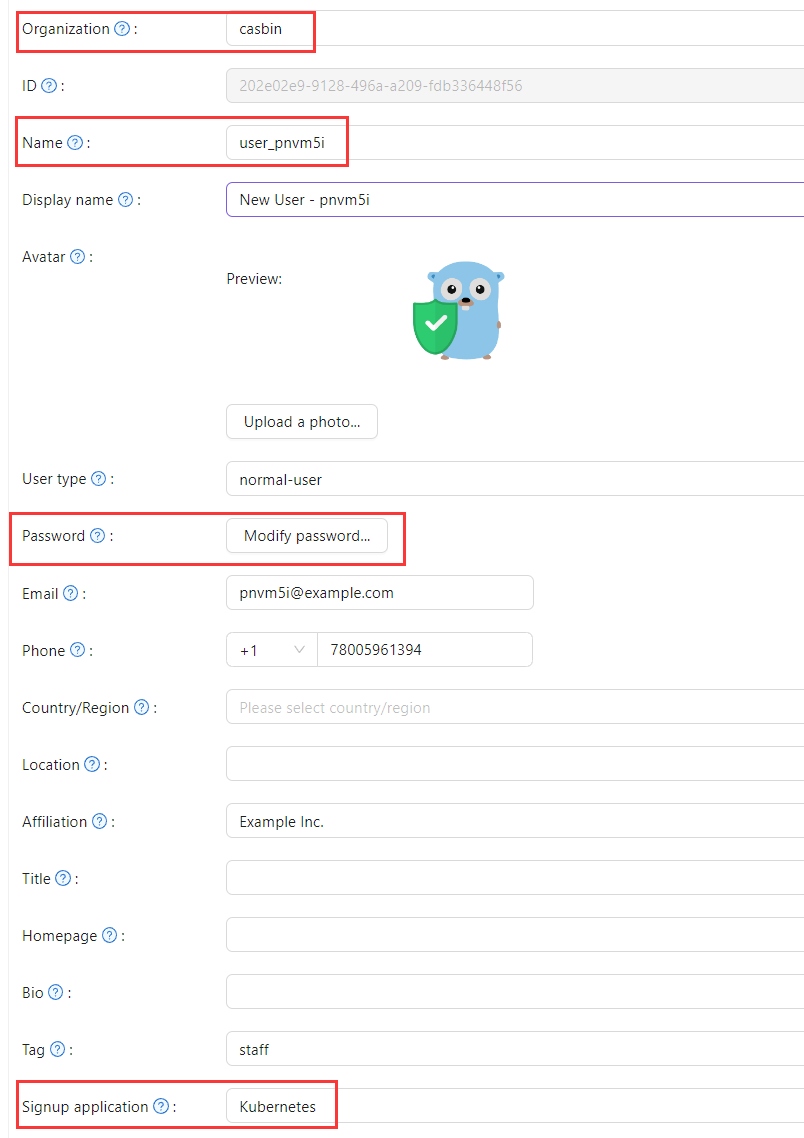
Next, add a new user to the application that you just created.
Please note that the Organization and Signup application used here should correspond to the app registered earlier.
Step 2: Configure Kubernetes API Server with OIDC Authentication
To enable the OIDC plugin, you need to configure the following flags on the API server:
--oidc-issuer-url: URL of the provider that allows the API server to discover public signing keys.--oidc-client-id: A client id that all tokens must be issued for.
This article uses minikube for demonstration. You can configure the OIDC plugin for the minikube's API server using the following command at startup:
minikube start --extra-config=apiserver.oidc-issuer-url=https://demo.casdoor.com --extra-config=apiserver.oidc-client-id=294b09fbc17f95daf2fe
Step 3: Test OIDC Authentication
Obtain Authentication Information
Due to the lack of a frontend in kubectl,
authentication can be performed by sending a POST request to the Casdoor server.
Here is the code in Python which sends a POST request to the Casdoor server
and retrieves the id_token and refresh_token:
import requests
import json
url = "https://demo.casdoor.com/api/login/oauth/access_token"
payload = json.dumps({
"grant_type": "password",
"client_id": "Kubernetes",
"client_secret": "72c65c3912aec24a9f3ec41b65a7577114ed2bae",
"username": "user_3u94sf",
"password": "123456"
})
response = requests.request("POST", url, data=payload)
print(response.text)
After executing this code, you should receive a response similar to the following:
{
"access_token": "xxx",
"id_token": "yyy",
"refresh_token": "zzz",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 72000,
"scope": ""
}
Now, you can use the id_token that you just obtained to authenticate with the Kubernetes API server.
HTTP Request-Based Authentication
Add the token to the request header.
curl https://www.xxx.com -k -H "Authorization: Bearer $(id_token)"
https://www.xxx.comis the Kubernetes API server deployment address.
Kubectl Client-Based Authentication
Configuration File Method
Write the following configuration to the ~/.kube/config file.
You should replace each configuration item in the configuration file above with the values you obtained earlier.
users:
- name: minikube
user:
auth-provider:
config:
client-id: Kubernetes
client-secret: 72c65c3912aec24a9f3ec41b65a7577114ed2bae
id-token: $(id_token)
idp-issuer-url: https://demo.casdoor.com
refresh-token: $(refresh_token)
name: oidc
Now, you can directly access your API server using kubectl. Try running a test command.
kubectl cluster-info
Command Line Argument Method
Alternatively, you can authenticate by directly adding the id_token to the command line parameters of kubectl.
kubectl --token=$(id_token) cluster-info